




Lutjanus mahogoni
| Ecological Descriptors |
||||
| Habitat | Size (cm)) | Diet | Behaviour | Sex |
| R, Co, (S) | 45 | Pisc, Cru Noct | Sh | F |
Description:
Adult: Silver to white, often with reddish tinge. Less robust, longer pointed head and slimmer body than many other Snappers. Reddish border on pelvic, dorsal and anal fins. Reddish margin on tail.
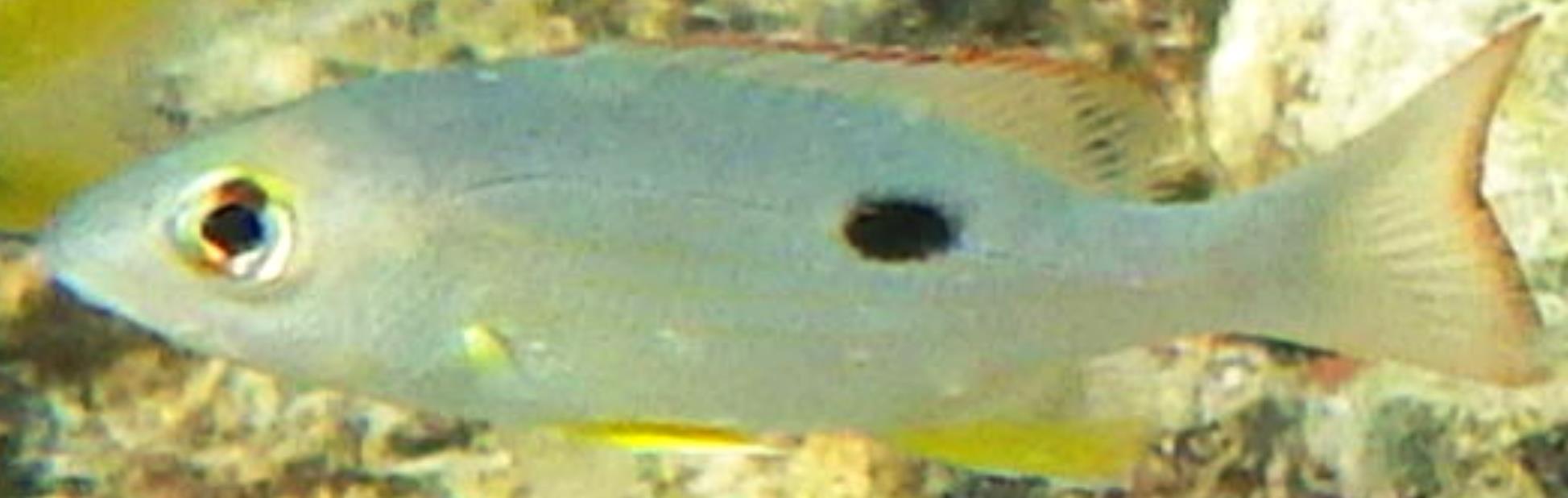
Juvenile: Juvenile has a black smudge on it's side and thin yellow stripes on body (those on the Lane Snapper are thicker). They are sometimes difficult to tell from the juvenile Lane Snapper, Lutjanus synagris, which also have a spot, yellow pectoral fins and dorsal and pectoral fins that have a reddish edging. .
Ecology
Adults inhabit clear shallow waters over rocky bottoms in the vicinity of coral reefs, less frequently in sandy or seagrass areas. They often form large aggregations during the day. They feed at night mainly on small fish, shrimps, crabs and cephalopods. Depth range 0-120m (0-400ft).
Life Cycle
Spawning occurs during the months of May, June, and July throughout the mahogany snapper’s range. Pelagic eggs are released and dispersed by ocean currents. Post fetilisation, eggs hatch within a day. Little is known about the larvae, but that they are planktonic; lengths <10 mm. They eventually settle out of the plankton, onto suitable habitat that offers some protection from predators. Juveniles have been described as pale with pink to red pigmentation on the distal portions of the median fins, and a prominent spot on the upper back.
Adult: Silver to white, often with reddish tinge. Less robust, longer pointed head and slimmer body than many other Snappers. Reddish border on pelvic, dorsal and anal fins. Reddish margin on tail.
Juvenile: Juvenile has a black smudge on it's side and thin yellow stripes on body (those on the Lane Snapper are thicker). They are sometimes difficult to tell from the juvenile Lane Snapper, Lutjanus synagris, which also have a spot, yellow pectoral fins and dorsal and pectoral fins that have a reddish edging. .
Ecology
Adults inhabit clear shallow waters over rocky bottoms in the vicinity of coral reefs, less frequently in sandy or seagrass areas. They often form large aggregations during the day. They feed at night mainly on small fish, shrimps, crabs and cephalopods. Depth range 0-120m (0-400ft).
Life Cycle
Spawning occurs during the months of May, June, and July throughout the mahogany snapper’s range. Pelagic eggs are released and dispersed by ocean currents. Post fetilisation, eggs hatch within a day. Little is known about the larvae, but that they are planktonic; lengths <10 mm. They eventually settle out of the plankton, onto suitable habitat that offers some protection from predators. Juveniles have been described as pale with pink to red pigmentation on the distal portions of the median fins, and a prominent spot on the upper back.
Mahogony Snapper
Juvenile
Juvenile
Mahogony Snapper



352

82



